Again this is a great googly questions that Interviewer ask : What is the difference between LUN mapping and LUN masking:
LUN Mapping:
The name itself speak to map a LUN to the Host (server). In SAN environment,
there are series of steps to be performed before any LUN mapping can be done to the Host
Requirement for LUN mapping:
Target: Target is usually on Storage side, the target is a port on storage side
After you have WWN of both 1. Initiator and 2. Target
Now you have to zone it unless at the Storage end you will not able to see the Hosts and will not able to Map.
I will discuss Zoning in different post.
Zoning is done on fabric switch which binds the Initiator to the target
LUN Masking:
LUN masking is more in security of the data meaning it Masks the LUN (Logical Unit Number) from the Host which is not meant for.
Eg:
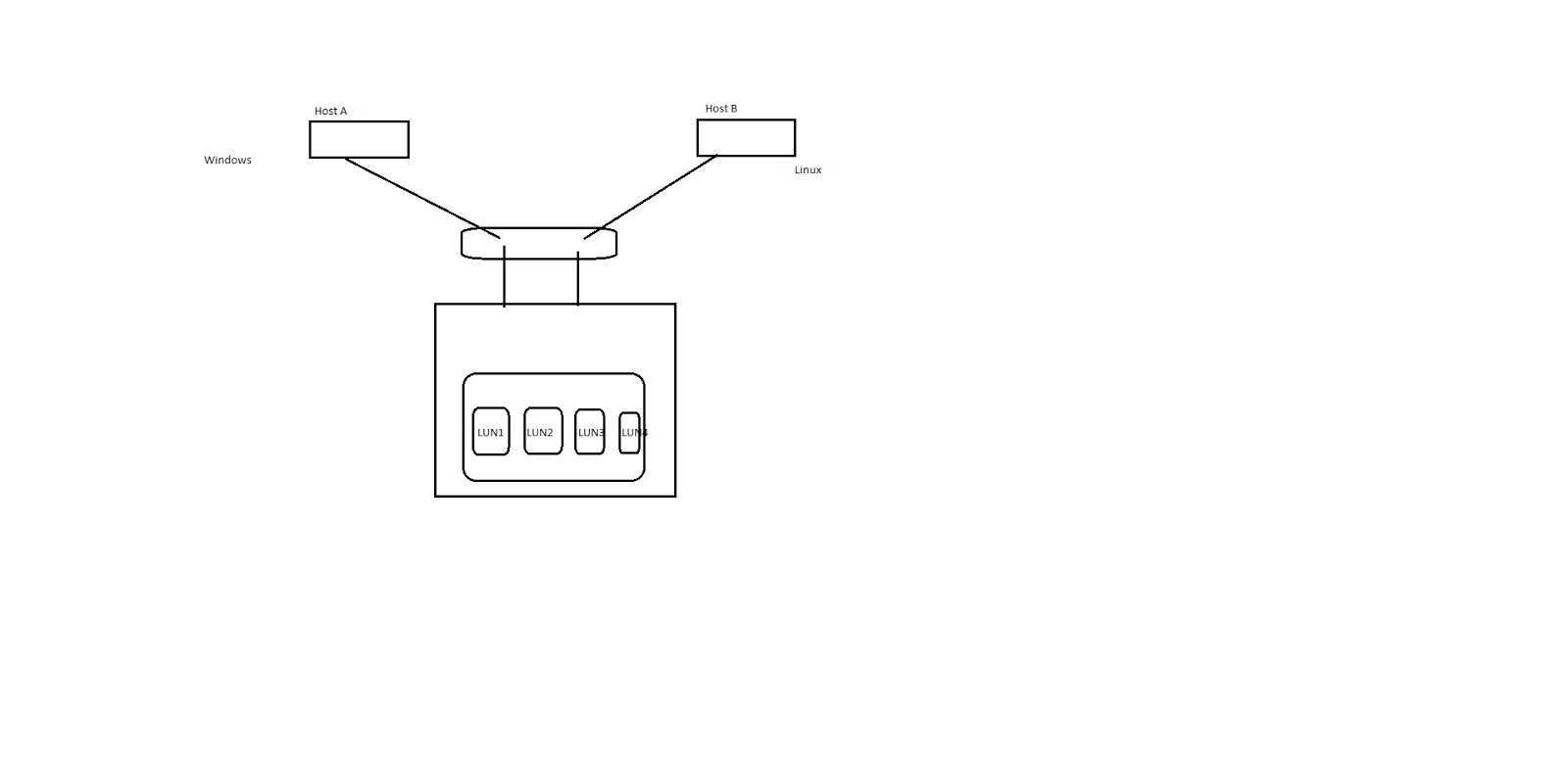
Suppose I have 2 Hosts A & B and 4 LUNs named LUN1 to LUN 4
2 LUN's (LUN 1 and LUN 2)are mapped to one host which is a windows Host and other 2 LUN's are mapped to Host B which is a Linux Host.
Now due to Data Confidentiality you don't want that Host A should see the LUN 3 and LUN 4 so restricting the access to Host A.
LUN Mapping:
The name itself speak to map a LUN to the Host (server). In SAN environment,
there are series of steps to be performed before any LUN mapping can be done to the Host
Requirement for LUN mapping:
- Initiator WWN (World Wide Name)
- Target WWN
- Zoning
Initiator: Initiator is itself a hard coded 64 bit digit embedded on HBA (host bus adapter). Think of this like a MAC address in TCP/IP scenario. It is unique for every HBA. Initiator is always on Host (server).
Below indicates here in below picture each HBA card connected to Fibre Channel
Here you can see clearly that there are 2 HBA cards and in each card there are two HBA ports.
Target: Target is usually on Storage side, the target is a port on storage side
After you have WWN of both 1. Initiator and 2. Target
Now you have to zone it unless at the Storage end you will not able to see the Hosts and will not able to Map.
I will discuss Zoning in different post.
Zoning is done on fabric switch which binds the Initiator to the target
LUN Masking:
LUN masking is more in security of the data meaning it Masks the LUN (Logical Unit Number) from the Host which is not meant for.
Eg:
Suppose I have 2 Hosts A & B and 4 LUNs named LUN1 to LUN 4
2 LUN's (LUN 1 and LUN 2)are mapped to one host which is a windows Host and other 2 LUN's are mapped to Host B which is a Linux Host.
Now due to Data Confidentiality you don't want that Host A should see the LUN 3 and LUN 4 so restricting the access to Host A.
 |
| Add caption |


